Redis单实例用于分布式锁的方案,在对可靠性要求不够高的场景下已经被大量应用,然而此方案存在一些缺陷,其作者提出了一种新的基于redis多实例的改进版算法。
1. Redis单实例作为分布式锁存在什么问题?
单点故障。假设Redis实例crash了,依赖获取锁后进行相应工作的业务逻辑无法执行。
互斥问题。进程A取锁,进入业务逻辑工作,此时Redis实例恰好crash并快速恢复了。进程B立即取到锁,也进入了业务逻辑。Boom,分布式锁的互斥性得不到保证了。
2. 新版Redlock算法的思路是什么?
- It gets the current time in milliseconds.
客户端获取当前时间(毫秒)- It tries to acquire the lock in all the N instances sequentially, using the same key name and random value in all the instances. During step 2, when setting the lock in each instance, the client uses a timeout which is small compared to the total lock auto-release time in order to acquire it. For example if the auto-release time is 10 seconds, the timeout could be in the ~ 5-50 milliseconds range. This prevents the client from remaining blocked for a long time trying to talk with a Redis node which is down: if an instance is not available, we should try to talk with the next instance ASAP.
用同一个key+随机value顺序向N个redis实例取NX锁,取NX锁的timeout相比redlock锁的release时间要小得多(毫秒级),若某个redis实例crash客户端能快速越过- The client computes how much time elapsed in order to acquire the lock, by subtracting from the current time the timestamp obtained in step 1. If and only if the client was able to acquire the lock in the majority of the instances (at least 3), and the total time elapsed to acquire the lock is less than lock validity time, the lock is considered to be acquired.
当且仅当获取半数以上redis实例的NX锁,且获取NX锁的总耗时(利用当前时间减去第一步的时间)小于redlock锁的release时间,获取redlock锁成功- If the lock was acquired, its validity time is considered to be the initial validity time minus the time elapsed, as computed in step 3.
- If the client failed to acquire the lock for some reason (either it was not able to lock N/2+1 instances or the validity time is negative), it will try to unlock all the instances (even the instances it believed it was not able to lock).
如果获取redlock锁失败,主动释放各个redis实例已经获取的NX锁
3. Martin认为以上算法存在什么问题?
分布式领域的专家在他的博客对分布式算法redlock提出质疑,质疑点如下。
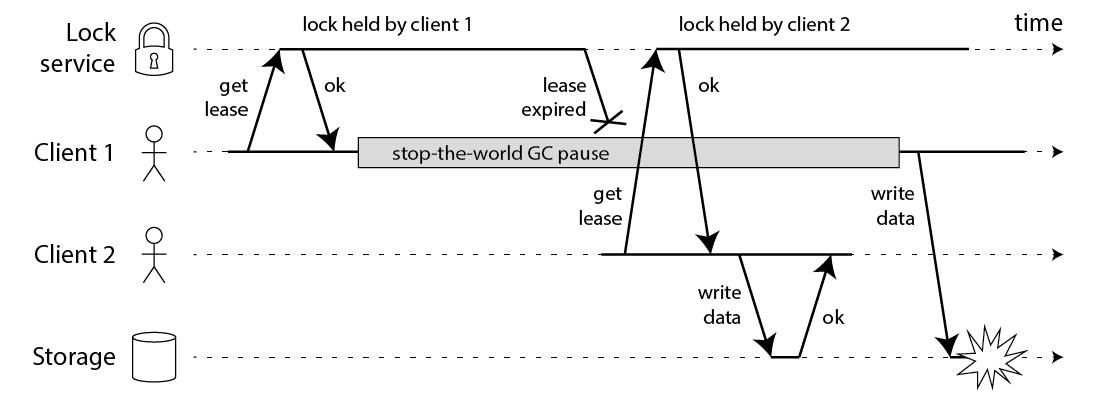
互斥性问题。见下图。Client1获取锁后进入STW,STW后锁已经超时,但Client1仍然认为自己持有锁。antirez在他的博客回应可以通过时间的double check来规避这个问题,但Martin提出,STW可能在任何情况下发生,更甚的是网络导致的延迟更是程序难以规避的,检查时间根本没用。Martin在他的博客提出了fencing的解决方案,详见他的博客。
时钟依赖问题。Martin提到Redis依赖于系统调用gettimeofday来判断NX锁是否超时,gettimeofday的可靠性堪忧,某些情况下如NTP校时会导致NX锁的提前或延后超时,Martin在他的博客提出这也会导致互斥问题。
直觉上来讲,redlock算法在上述第3步,获取锁的时间虽然没超时,但获取锁的时间占据了redlock锁release时间的大部分,此时还有进行下去的必要吗?
4. antirez的回应有哪些亮点?
为什么NX锁的value要用随机值?可以通过lua脚本原子性的释放锁。
客户端获取redlock锁失败后,应休眠random delay后重试,防止多客户端在同一时间又去竞争锁,竞态得不到缓解。
如果N个redis实例其中某一个crash了,可以为其设置一个delay start,防止它恢复后突然加入打破现有的平衡。也可以考虑设置fsync,这样每次redis数据修改都会落盘。